
- Excel Functions - Home
- Compatibility Functions
- Compatibility Functions
- BETADIST Function
- BETAINV Function
- BINOMDIST Function
- CEILING Function
- CHIDIST Function
- CHIINV Function
- CHITEST Function
- CONFIDENCE Function
- COVAR Function
- CRITBINOM Function
- EXPONDIST Function
- FDIST Function
- FINV Function
- FLOOR Function
- FTEST Function
- GAMMADIST Function
- GAMMAINV Function
- HYPGEOMDIST Function
- LOGINV Function
- LOGNORMDIST Function
- MODE Function
- NEGBINOMDIST Function
- NORMDIST Function
- NORMINV Function
- NORMSDIST Function
- NORMSINV Function
- PERCENTILE Function
- PERCENTRANK Function
- POISSON Function
- QUARTILE Function
- RANK Function
- STDEV Function
- STDEVP Function
- TDIST Function
- TINV Function
- TTEST Function
- VAR Function
- VARP Function
- WEIBULL Function
- ZTEST Function
- Logical Functions
- Logical Functions
- AND Function
- FALSE Function
- IF Function
- IFERROR Function
- IFNA Function
- IFS Function
- NOT Function
- OR Function
- SWITCH Function
- TRUE Function
- XOR Function
- Text Functions
- Text Functions
- ARRAYTOTEXT Function
- BAHTTEXT Function
- CHAR Function
- CLEAN Function
- CODE Function
- CONCAT Function
- CONCATENATE Function
- DBCS Function
- DOLLAR Function
- Exact Function
- FIND Function
- FINDB Function
- FIXED Function
- LEFT Function
- LEFTB Function
- LEN Function
- LENB Function
- LOWER Function
- MID Function
- MIDB Function
- NUMBERVALUE Function
- PHONETIC Function
- PROPER Function
- REPLACE Function
- REPLACEB Function
- REPT Function
- RIGHT Function
- RIGHTB Function
- SEARCH Function
- SEARCHB Function
- SUBSTITUTE Function
- T Function
- TEXT Function
- TEXTAFTER Function
- TEXTBEFORE Function
- TEXTJOIN Function
- TEXTSPLIT Function
- TRIM Function
- UNICHAR Function
- UNICODE Function
- UPPER Function
- VALUE Function
- VALUETOTEXT Function
- Date & Time Functions
- Date & Time Functions
- DATE Function
- DATEDIF Function
- DATEVALUE Function
- DAY Function
- DAYS Function
- DAYS360 Function
- EDATE Function
- EOMONTH Function
- HOUR Function
- ISOWEEKNUM Function
- MINUTE Function
- MONTH Function
- NETWORKDAYS Function
- NETWORKDAYS.INTL Function
- NOW Function
- SECOND Function
- TIME Function
- TIMEVALUE Function
- TODAY Function
- WEEKDAY Function
- WEEKNUM Function
- WORKDAY Function
- WORKDAY.INTL Function
- YEAR Function
- YEARFRAC Function
- Cube Functions
- Cube Functions
- CUBEKPIMEMBER Function
- CUBEMEMBER Function
- CUBEMEMBERPROPERTY Function
- CUBERANKEDMEMBER Function
- CUBESET Function
- CUBESETCOUNT Function
- CUBEVALUE Function
- Math Functions
- Math Functions
- ABS Function
- AGGREGATE Function
- ARABIC Function
- BASE Function
- CEILING.MATH Function
- COMBIN Function
- COMBINA Function
- DECIMAL Function
- DEGREES Function
- EVEN Function
- EXP Function
- FACT Function
- FACTDOUBLE Function
- FLOOR.MATH Function
- GCD Function
- INT Function
- LCM Function
- LN Function
- LOG Function
- LOG10 Function
- MDETERM Function
- MINVERSE Function
- MMULT Function
- MOD Function
- MROUND Function
- MULTINOMIAL Function
- MUNIT Function
- ODD Function
- PI Function
- POWER Function
- PRODUCT Function
- QUOTIENT Function
- RADIANS Function
- RAND Function
- RANDBETWEEN Function
- ROMAN Function
- ROUND Function
- ROUNDDOWN Function
- ROUNDUP Function
- SERIESSUM Function
- SIGN Function
- SQRT Function
- SQRTPI Function
- SUBTOTAL Function
- SUM Function
- SUMIF Function
- SUMIFS Function
- SUMPRODUCT Function
- SUMSQ Function
- SUMX2MY2 Function
- SUMX2PY2 Function
- SUMXMY2 Function
- TRUNC Function
- Trigonometric Functions
- Trigonometric Functions
- ACOS
- ACOSH Function
- ACOT Function
- ACOTH Function
- ASIN Function
- ASINH Function
- ATAN Function
- ATAN2 Function
- ATANH Function
- COS Function
- COSH Function
- COT Function
- COTH Function
- CSC Function
- CSCH Function
- SEC Function
- SECH Function
- SIN Function
- SINH Function
- TAN Function
- TANH Function
- Database Functions
- Database Functions
- DAVERAGE
- DCOUNT
- DCOUNTA
- DGET
- DMAX
- DMIN
- DPRODUCT
- DSTDEV
- DSTDEVP
- DSUM
- DVAR
- DVARP
- Dynamic Array Functions
- Dynamic Array Functions
- FILTER Function
- RANDARRAY Function
- SEQUENCE Function
- SORT Function
- SORTBY Function
- UNIQUE Function
- XLOOKUP Function
- XMATCH Function
- Engineering Functions
- Engineering Functions
- BESSELI Function
- BESSELJ Function
- BESSELK Function
- BESSELY Function
- BIN2DEC Function
- BIN2HEX Function
- BIN2OCT Function
- BITAND Function
- BITLSHIFT Function
- BITOR Function
- BITRSHIFT Function
- BITXOR Function
- COMPLEX Function
- CONVERT Function
- DEC2BIN Function
- DEC2HEX Function
- DEC2OCT Function
- DELTA Function
- ERF Function
- ERF.PRECISE Function
- ERFC Function
- ERFC.PRECISE Function
- GESTEP Function
- HEX2BIN Function
- HEX2DEC Function
- HEX2OCT Function
- IMABS Function
- IMAGINARY Function
- IMARGUMENT Function
- IMCONJUGATE Function
- IMCOS Function
- IMCOSH Function
- IMCOT Function
- IMCSC Function
- IMCSCH Function
- IMDIV Function
- IMEXP Function
- IMLN Function
- IMLOG2 Function
- IMLOG10 Function
- IMPOWER Function
- IMPRODUCT Function
- IMREAL Function
- IMSEC Function
- IMSECH Function
- IMSIN Function
- IMSINH Function
- IMSQRT Function
- IMSUB Function
- IMSUM Function
- IMTAN Function
- OCT2BIN Function
- OCT2DEC Function
- OCT2HEX Function
- Financial Functions
- Financial Functions
- ACCRINT Function
- ACCRINTM Function
- AMORDEGRC Function
- AMORLINC Function
- COUPDAYBS Function
- COUPDAYS Function
- COUPDAYSNC Function
- COUPNCD Function
- COUPNUM Function
- COUPPCD Function
- CUMIPMT Function
- CUMPRINC Function
- DB Function
- DDB Function
- DISC Function
- DOLLARDE Function
- DOLLARFR Function
- DURATION Function
- EFFECT Function
- FV Function
- FVSCHEDULE Function
- INTRATE Function
- IPMT Function
- IRR Function
- ISPMT Function
- MDURATION Function
- MIRR Function
- NOMINAL Function
- NPER Function
- NPV Function
- ODDFPRICE Function
- ODDFYIELD Function
- ODDLPRICE Function
- ODDLYIELD Function
- PDURATION Function
- PMT Function
- PPMT Function
- PRICE Function
- PRICEDISC Function
- PRICEMAT Function
- PV Function
- RATE Function
- RECEIVED Function
- RRI Function
- SLN Function
- SYD Function
- TBILLEQ Function
- TBILLPRICE Function
- TBILLYIELD Function
- VDB Function
- XIRR Function
- XNPV Function
- YIELD Function
- YIELDDISC Function
- YIELDMAT Function
- Information Functions
- Information Functions
- CELL Function
- ERROR.TYPE Function
- INFO Function
- ISBLANK Function
- ISERR Function
- ISERROR Function
- ISEVEN Function
- ISFORMULA Function
- ISLOGICAL Function
- ISNA Function
- ISNONTEXT Function
- ISNUMBER Function
- ISODD Function
- ISREF Function
- ISTEXT Function
- N Function
- NA Function
- SHEET Function
- SHEETS Function
- TYPE Function
- Lookup & Reference Functions
- Lookup & Reference Functions
- ADDRESS Function
- AREAS Function
- CHOOSE Function
- COLUMN Function
- COLUMNS Function
- FORMULATEXT Function
- GETPIVOTDATA Function
- HLOOKUP Function
- HYPERLINK Function
- INDEX Function
- INDIRECT Function
- LOOKUP Function
- MATCH Function
- OFFSET Function
- ROW Function
- ROWS Function
- RTD Function
- TRANSPOSE Function
- VLOOKUP Function
- Statistical Functions
- Statistical Functions
- AVEDEV Function
- AVERAGE Function
- AVERAGEA Function
- AVERAGEIF Function
- AVERAGEIFS Function
- BETA.DIST Function
- BETA.INV Function
- BINOM.DIST Function
- BINOM.DIST.RANGE Function
- BINOM.INV Function
- CHISQ.DIST Function
- CHISQ.DIST.RT Function
- CHISQ.INV Function
- CHISQ.INV.RT Function
- CHISQ.TEST Function
- CONFIDENCE.NORM Function
- CONFIDENCE.T Function
- CORREL Function
- COUNT Function
- COUNTA Function
- COUNTBLANK Function
- COUNTIF Function
- COUNTIFS Function
- COVARIANCE.P Function
- COVARIANCE.S Function
- DEVSQ Function
- EXPON.DIST Function
- F.DIST Function
- F.DIST.RT Function
- F.INV Function
- F.INV.RT Function
- F.TEST Function
- FISHER Function
- FISHERINV Function
- FORECAST Function
- FORECAST.ETS Function
- FORECAST.ETS.CONFINT Function
- FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY Function
- FORECAST.ETS.STAT Function
- FORECAST.LINEAR Function
- FREQUENCY Function
- GAMMA Function
- GAMMA.DIST Function
- GAMMA.INV Function
- GAMMALN Function
- GAMMALN.PRECISE Function
- GAUSS Function
- GEOMEAN
- GROWTH
- HARMEAN
- HYPGEOM.DIST
- INTERCEPT Function
- KURT Function
- LARGE Function
- LINEST Function
- LOGEST Function
- LOGNORM.DIST Function
- LOGNORM.INV Function
- MAX Function
- MAXA Function
- MAXIFS Function
- MEDIAN Function
- MIN Function
- MINA Function
- MINIFS Function
- MODE.MULT Function
- MODE.SNGL Function
- NEGBINOM.DIST Function
- NORM.DIST Function
- NORM.INV Function
- NORM.S.DIST Function
- NORM.S.INV Function
- PEARSON Function
- PERCENTILE.EXC
- PERCENTILE.INC
- PERCENTRANK.EXC
- PERCENTRANK.INC
- PERMUT
- PERMUTATIONA
- PHI
- POISSON.DIST
- PROB
- QUARTILE.EXC
- QUARTILE.INC
- RANK.AVG
- RANK.EQ
- RSQ
- SKEW
- SKEW.P
- SLOPE
- SMALL
- STANDARDIZE
- STDEV.P
- STDEV.S
- STDEVA
- STDEVPA
- STEYX
- T.DIST
- T.DIST.2T
- T.DIST.RT
- T.INV
- T.INV.2T
- T.TEST
- TREND
- TRIMMEAN Function
- VAR.P Function
- VAR.S Function
- VARA Function
- VARPA Function
- WEIBULL.DIST Function
- Z.TEST Function
- Web Functions
- Web Functions
- ENCODEURL Function
- FILTERXML Function
- WEBSERVICE Function
Excel - TDIST Function
TDIST Function
The Excel TDIST function computes the T distribution across the small dataset and will return the Students t-distribution. The Excel-TDIST function permits you to look at the mean difference between two groups. For example, Is the mean gross pay for male employees greater than that of female employees?
If you are dealing with small datasets of less than 30 samples and are not aware of the sample standard deviation, then the T distribution is the best way to verify the null hypothesis and reach a conclusion.
T-test usually comes in two variations −
- One-tailed distribution
- Two-tailed distribution
The TDIST function interchanges with the T.DIST.2T & T.DIST.RT functions appended in Excel 2010.
Syntax
The syntax of TDIST function is as follows −
TDIST(x,deg_freedom,tails)
Arguments
You can use the following arguments with the TDIST function −
| Argument | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| X | It specifies the numeric value at which to evaluate the distribution. | Required |
| Deg_freedom | It specifies the integer value that indicates the number of degrees of freedom. | Required |
| Tails |
It can be either equal to integer 1 or 2. If Tails = 1, TDIST will retrieve the one-tailed distribution. If Tails = 2, TDIST will retrieve the two-tailed distribution. |
Required |
Points to Remember
- If Tails = 1, the TDIST function is evaluated as TDIST = P( X > x ), where X indicates the random variable. If Tails = 2, TDIST is calculated as TDIST = P(|X| > x) = P(X > x or X < -x)
- If Deg_Freedom argument is in decimal form, it is truncated to integers.
- If any argument is other than numeric, TDIST will retrieve the #VALUE! Error.
- If Deg_freedom is negative, TDIST will return the #NUM! Error.
- If the Tails argument contains an integer value other than either 1 or 2, then TDIST will retrieve the #NUM! Error.
- If the x value is negative, TDIST will retrieve the #NUM! Error.
Examples of TDIST Function
Practice the following examples to learn the use of the TDIST function in Excel.
Example 1
Step 1 − Consider the sample dataset, where the Mean and Standard Deviation of the two groups are specified in the range C2:D3. The significance level is 0.05. Lets calculate the Degree of freedom, which is equal to n-1. You may enter the formula =C8+D8-1 in the C10 cell and press the Enter key to obtain the resulting value.


Step 2 − After that, you may write the expression =ABS(C2-D2)/SQRT((C8*(1/C6+1/D6))) in the C10 cell to obtain the t calculated value and press the Enter key.

Therefore, the t calculated value is 2.407209.

Step 3 − Moreover, you may write the expression =TINV(2*C4,C10) in the C12 cell to get the t critical value by using the TINV function and press the Enter tab.

Therefore, the t critical value is 1.650538.

Step 4 − Finally, calculate the probability one-tailed t distribution by employing the TDIST function. Enter the formula =TDIST(C11,C10,1) in the C13 cell and press Enter.

Therefore, the probability value is .008374, which is greater than the significance level (.005). Thus, we accept the null hypothesis and fail to accept the alternative hypothesis.

Example 2
If Deg_Freedom argument is in decimal form, it is truncated to integers.
Solution
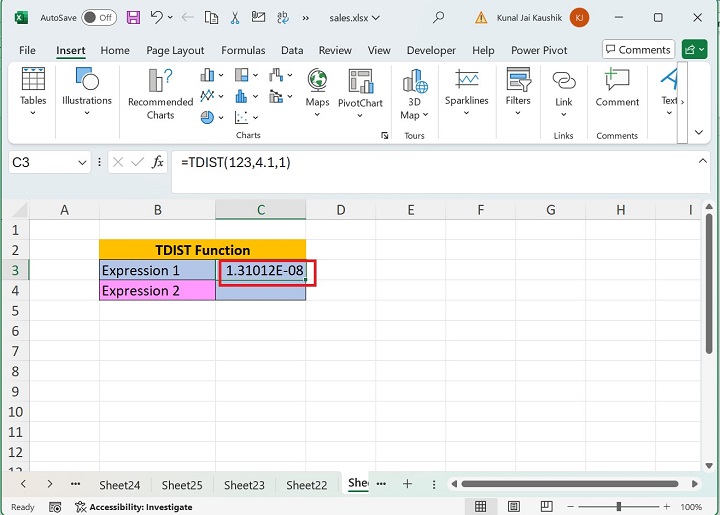
You may enter the TDIST formula =TDIST(123,4.1,1) in the C3 cell and press the Enter tab. In this expression, the second argument (Deg_freedom), whose value is 4.1, is truncated to 4 number.

Example 3
If any argument is other than numeric, TDIST will retrieve the #VALUE! Error.
Solution
Lets suppose you use the non-numeric value in any argument of the TDIST function; then, it will not give you an accurate result. Enter the TDIST formula =TDIST("ice",2,1) in the C3 cell and press the Enter tab.

Therefore, the TDIST function will generate the #VALUE error.

Example 4
If Deg_freedom is negative, TDIST will return the #NUM! Error.
Solution
In this example, you can enter the formula =TDIST(121.1,-4,1) in the C3 cell. Here, the second argument's value (Deg_of_freedom) is -4, which is not permittable.

After that, press the Enter tab to get the result.

Therefore, the TDIST function will obtain the #NUM! Function. You can edit the Deg_of_freedom value to a positive value for the correct result.
Example 5
If the Tails argument contains an integer value other than either 1 or 2, then TDIST will retrieve the #NUM! Error.
Solution
First, write the TDIST formula =TDIST(123,4,9) in the C4 cell. Here, the value of Tails(third argument) is 9, which generates the error once you execute this function.

You may press the Enter key to get the result.

As you can see in this screenshot, the TDIST function will create the #NUM! error.