Rendering of live Jupyter notebooks with interactive widgets.
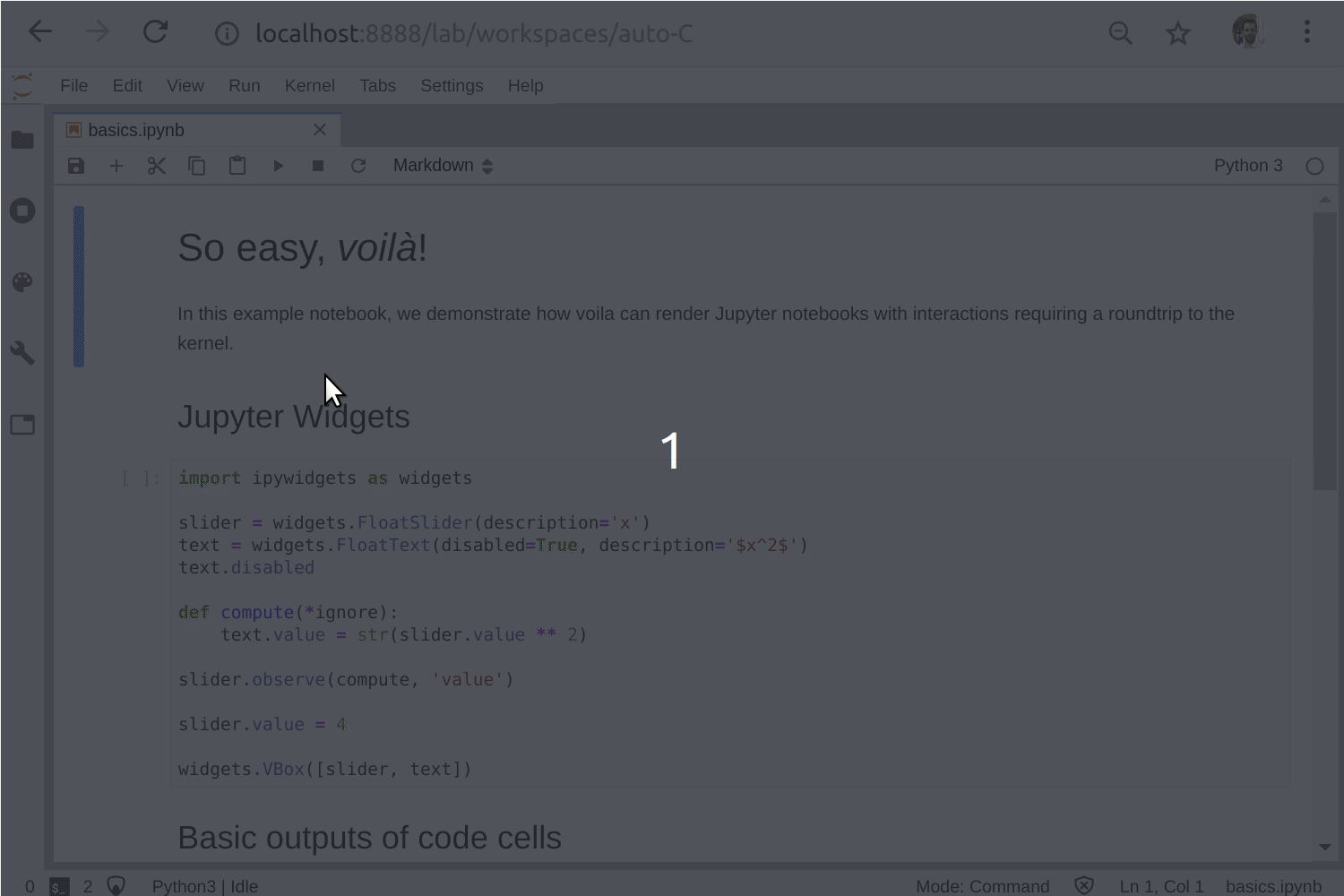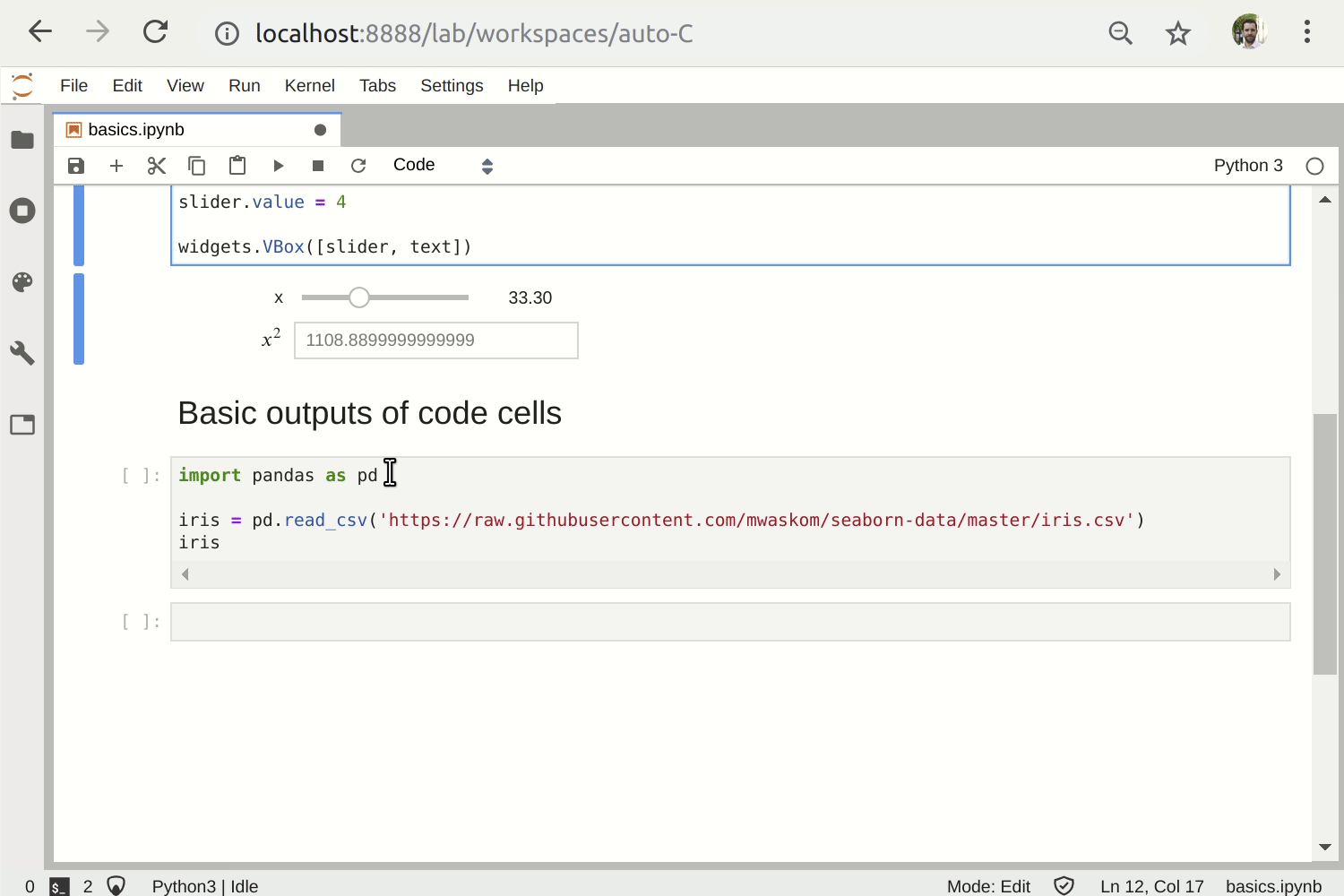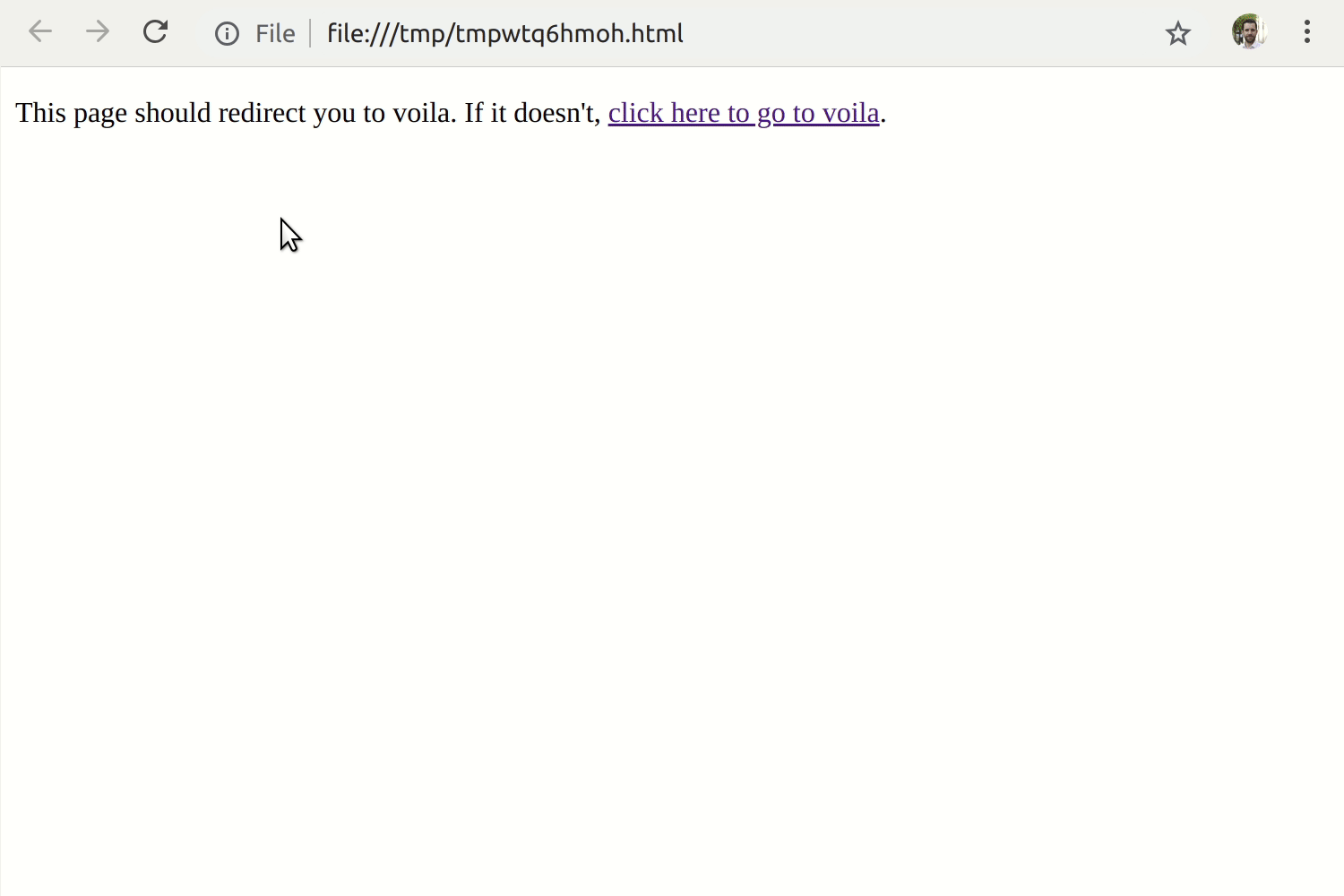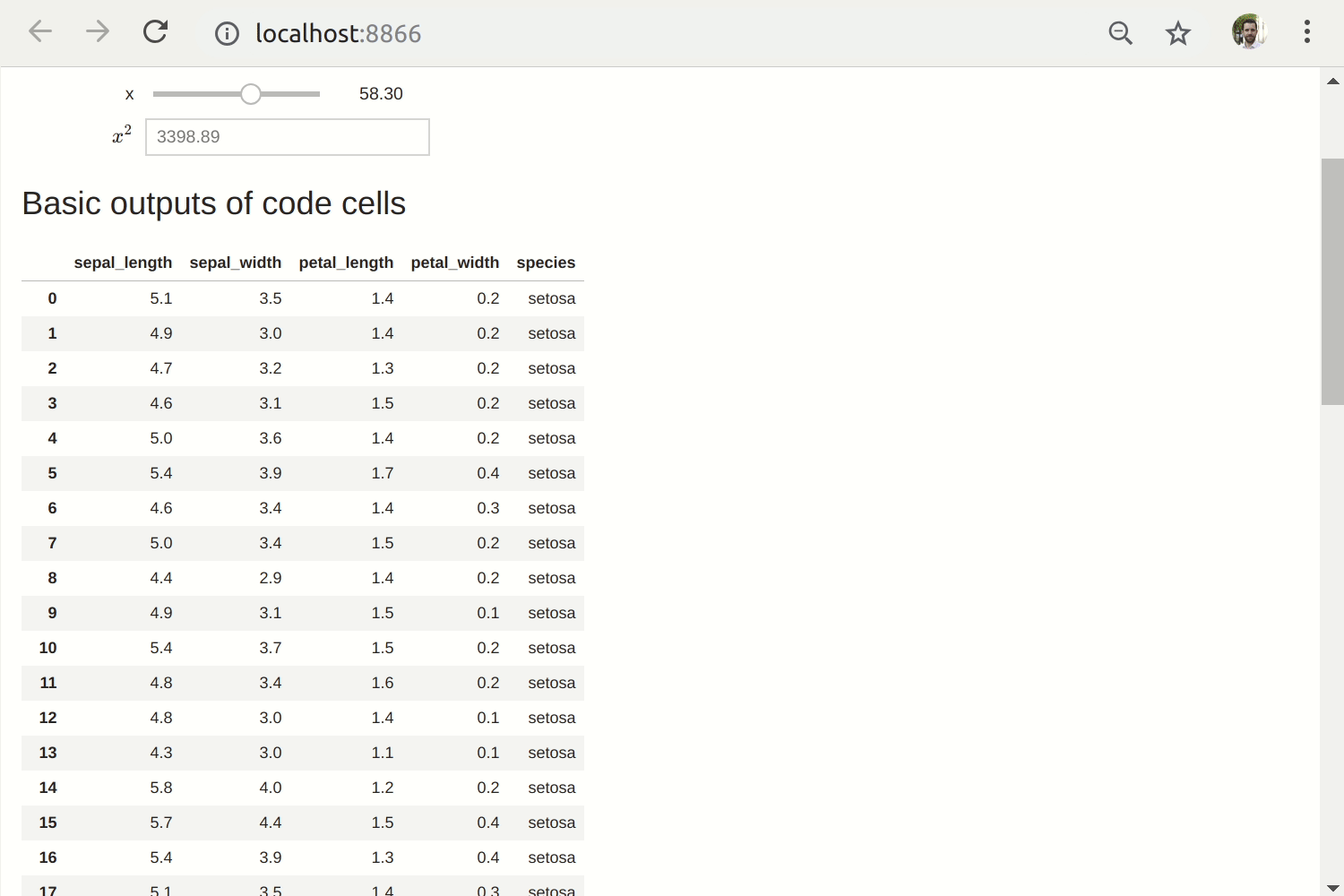
Voilà turns Jupyter notebooks into standalone web applications.
Unlike the usual HTML-converted notebooks, each user connecting to the Voilà tornado application gets a dedicated Jupyter kernel which can execute the callbacks to changes in Jupyter interactive widgets.
- By default, Voilà disallows execute requests from the front-end, preventing execution of arbitrary code.
- By default, Voilà runs with the
strip_sourcesoption, which strips out the input cells from the rendered notebook.
Voilà can be installed with the mamba (or conda) package manager from conda-forge
mamba install -c conda-forge voila
or from PyPI
pip install voila
Voilà provides a JupyterLab extension that displays a Voilà preview of your Notebook in a side-pane.
Starting with JupyterLab 3.0, the extension is automatically installed after installing voila
with pip install voila.
If you would like to install the extension from source, run the following command.
jupyter labextension install @voila-dashboards/jupyterlab-preview
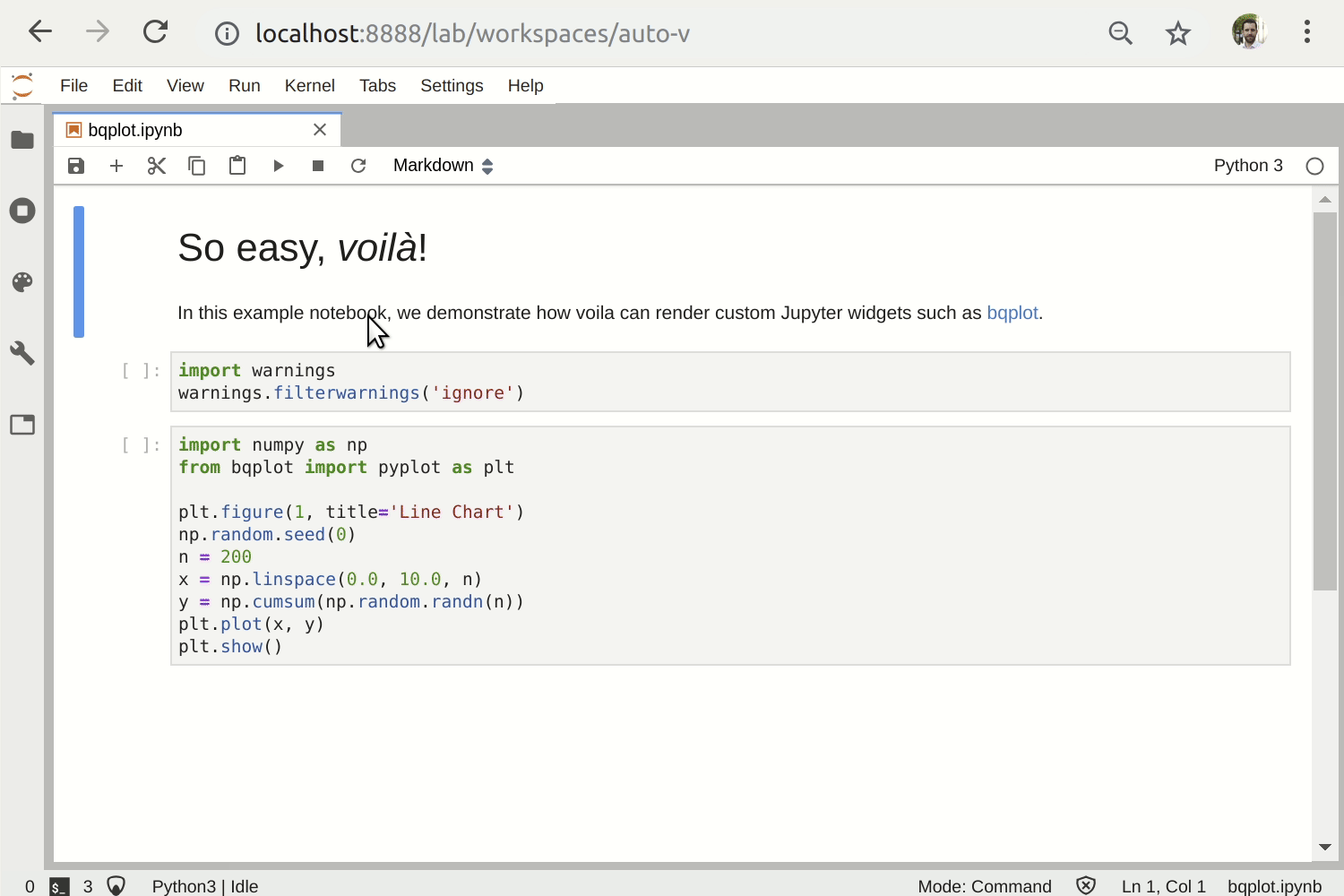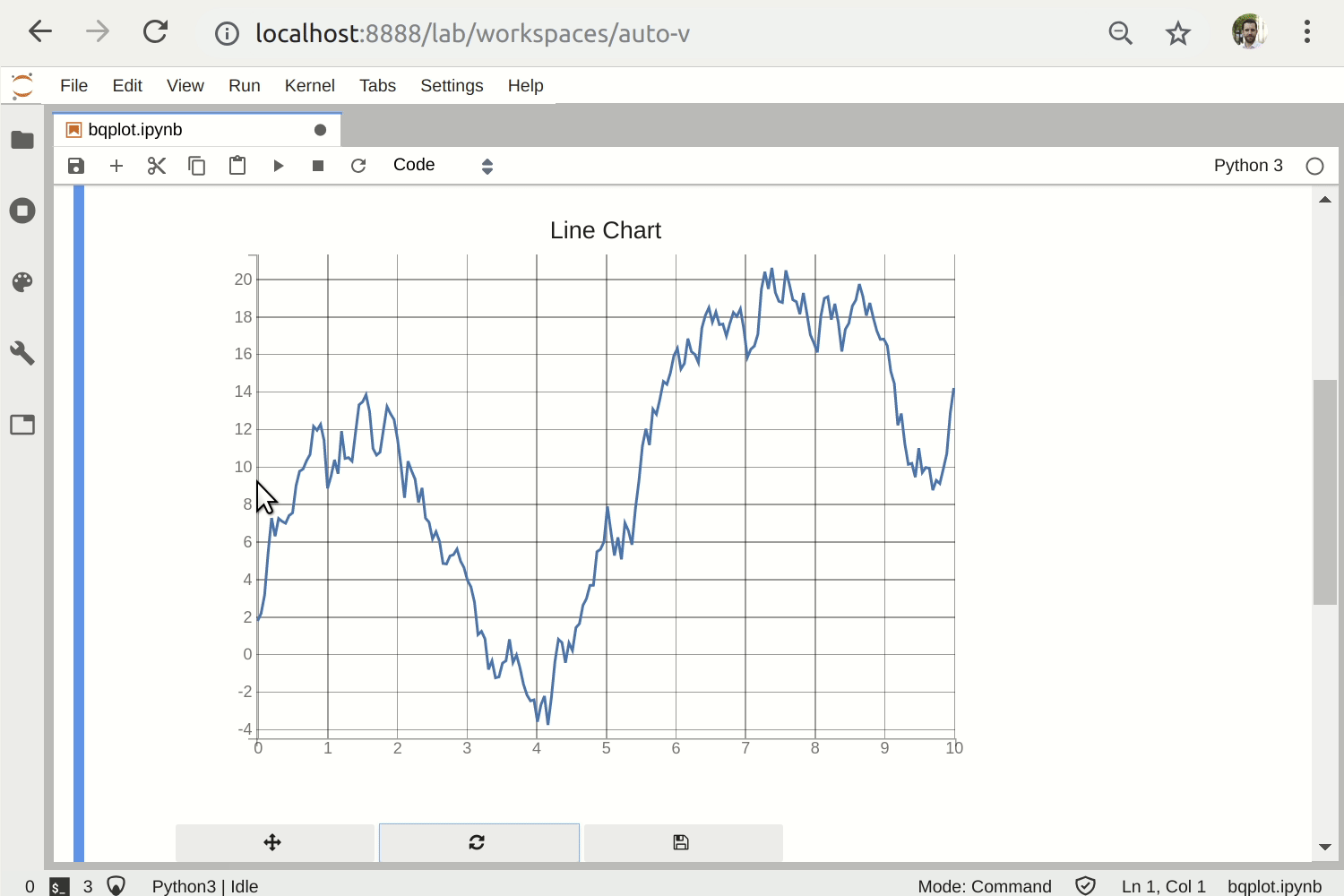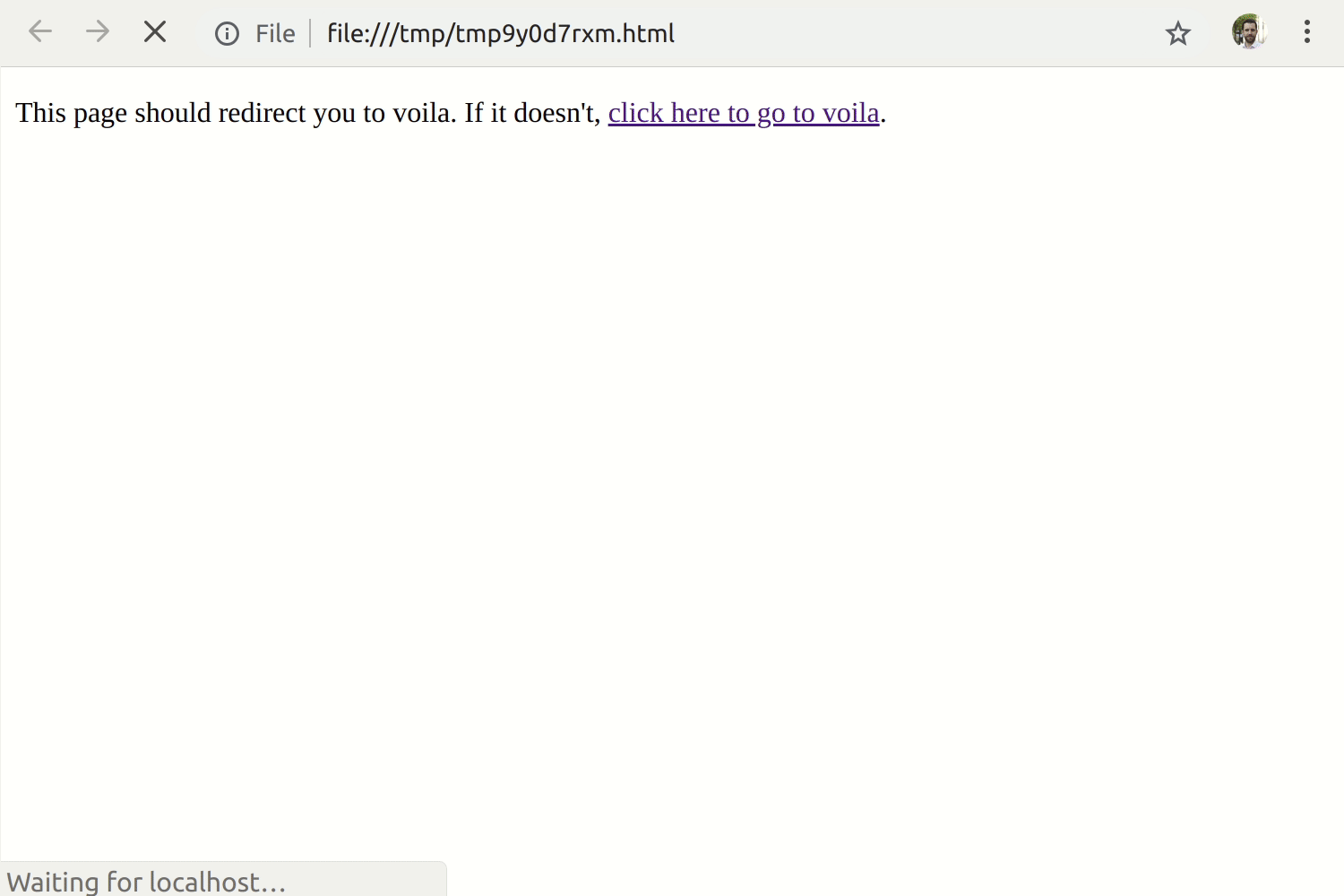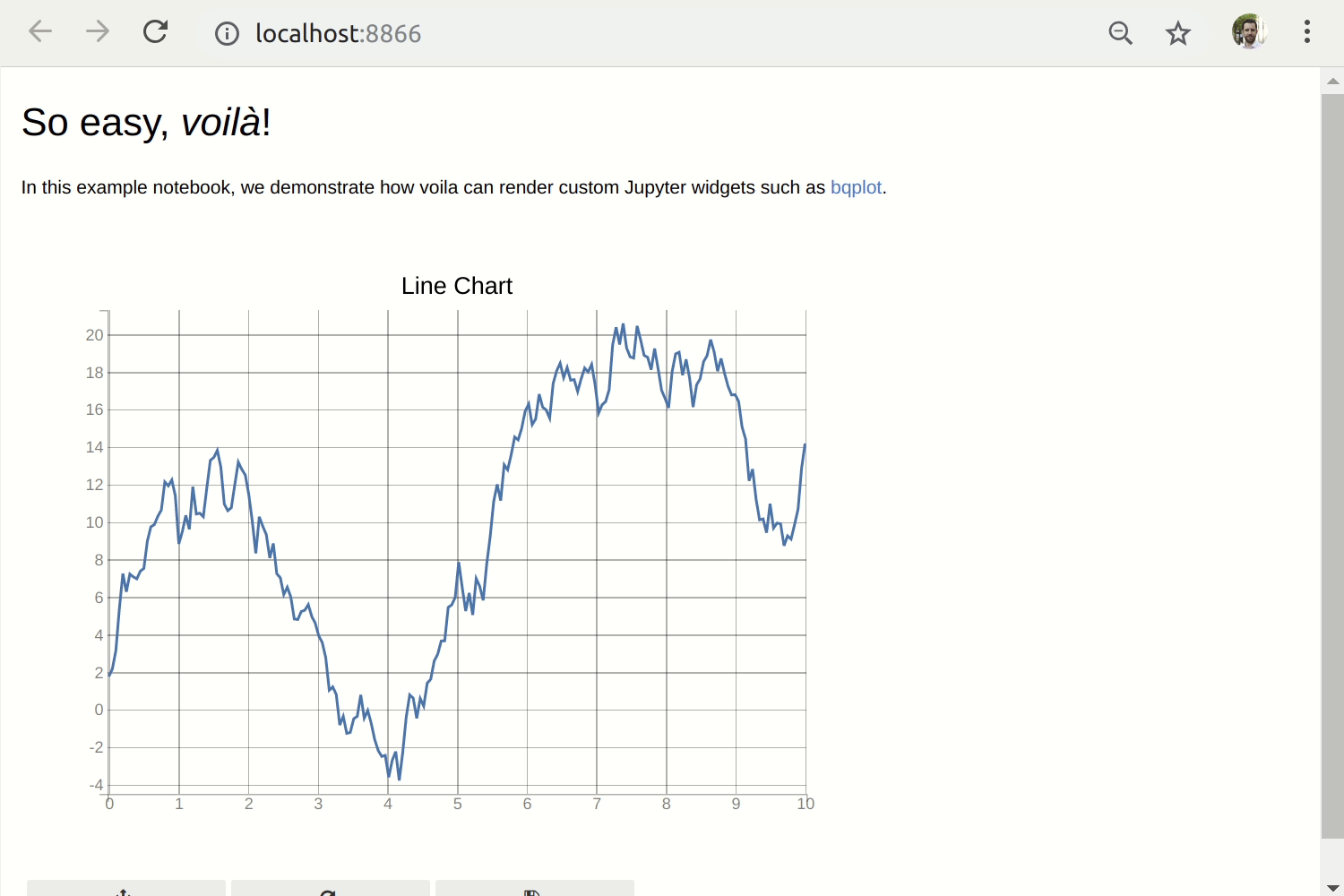
To render the bqplot example notebook as a standalone app, run
voila bqplot.ipynb.
To serve a directory of jupyter notebooks, run voila with no argument.
For example, to render the example notebook bqplot.ipynb from this repository with Voilà, you can first update your current environment with the requirements of this notebook (in this case in a conda environment and render the notebook with
mamba env update -f .binder/environment.yml
cd notebooks/
voila bqplot.ipynb
For more command line options (e.g., to specify an alternate port number),
run voila --help.
Voilà can also be used as a Jupyter server extension, both with the notebook server or with jupyter_server.
To install the Jupyter server extension, run
jupyter serverextension enable voila
jupyter server extension enable voila
When running the Jupyter server, the Voilà app is accessible from the base url
suffixed with voila.
To get started with using Voilà, check out the full documentation:
https://voila.readthedocs.io/
The following two examples show how a standalone Jupyter notebook can be turned into a separate app, from the command-line integration.
Rendering a notebook making use of a custom widget library (bqplot)
The sources of the Jupyter notebook can be displayed in a Voilà app if option strip_sources is set to False.
Voilà is built upon Jupyter standard formats and protocols, and is agnostic to the programming language of the notebook. In this example, we present an example of a Voilà application powered by the C++ Jupyter kernel xeus-cling, and the xleaflet project.
The Voilà Gallery is a collection of live dashboards and applications built with Voilà and Jupyter widgets.
Most of the examples rely on widget libraries such as ipywidgets, ipyleaflet, ipyvolume, bqplot and ipympl, and showcase how to build complex web applications entirely based on notebooks.
New examples can be added to the gallery by following the steps listed in the voila-gallery/gallery repository.
See CONTRIBUTING.md to know how to contribute and set up a development environment.
Voilà depends on nbconvert and jupyter_server.
We use a shared copyright model that enables all contributors to maintain the copyright on their contributions.
This software is licensed under the BSD-3-Clause license. See the LICENSE file for details.